In C++ programming there are different ways in which parameter data can be passed into and out of functions and methods. some of the ways are exclusive to only C++, while others are permissible in most programming languages. Understanding this concept is very crucial if you want to write efficient, systematic and well-structured code. Let's delve straight into it.
Pass by Value
The default parameter passing mechanism in C++ is classified as pass by value, also known as call by value. This means the value of the actual parameter(calling function) is copied to the corresponding non-pointer or no reference parameter known as the formal parameter(called function) to execute the function’s code. Since it is working on a copy of the actual parameter, the function’s execution cannot affect the value of the actual parameter owned by the caller.
#include <iostream>
// PASS BY VALUE
//formal parameter (int y)
void iteration(int y ) {
std::cout << "Beginning execution, y = " << y << '\n';
y++;
std::cout << "Ending execution of iteration, y = " << y << '\n';
}
int main(){
int y = 5;
std::cout << "Before iteration the value of, y = " << y << '\n';
iteration(y);
std::cout << "After iteration, y = " << y << '\n';
}
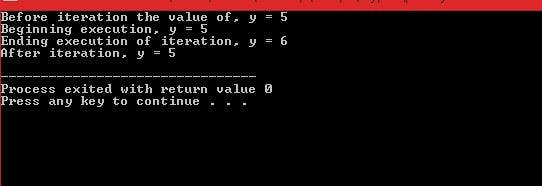
In the following example, the main function passes the value 5 to the iteration function. The function iteration receives a copy of the value and accesses it by the identifier y. The function iteration changes the value by incrementing it then control is passed back to the main.
Figure 1. The output result of a Pass By Value technique
The variable name of the actual parameter is the same as the formal parameter. Since the formal parameter is localized within its function. Both actual parameter and formal parameters are declared and used in different contexts and represent completely different memory locations, their names can be the same without any problems. The memory for the variable y in main is unaffected since increment works on a copy of the actual parameter.
Advantages of Pass by value
- One of the advantages of pass-by-value is that a function is free to modify a parameter without inadvertently changing the data at the calling location.
Disadvantages of Pass by value
When a function changes a parameter passed by value, that change cannot be propagated back to the caller through the parameter even when we want to do so.
Inefficiency in storage allocation- As the size of data increases, it takes longer to copy the data to the function.
Pass by Reference via References
Pass-by-reference means to pass the reference of an argument in the calling function to the corresponding formal parameter of the called function. The called function can modify the value of the argument by using its reference passed in.
The following example shows how arguments are passed by reference. The reference parameters are initialized with the actual arguments when the function is called. The reference is denoted by an '&' symbol.
For example, consider the following code snippet:
#include <iostream>
void increment(int& value) {
value++;
}
int main() {
int x = 5;
increment(x);
std::cout << x << std::endl; // Outputs 6
return 0;
}
In the above snippet, the increment function takes an int value passed by reference and increments it. When the increment function is called in the main function with the variable x, the value of x is changed and the output is 6.

Figure 2. The output result of a Pass By Reference technique
Pass by Pointer
Pass by pointer means passing the memory address of a variable to the function. When a variable is passed by a pointer, the function receives a pointer to the original variable, and any changes made to the variable within the function will be reflected in the original variable as well. The pointer is denoted by an '*' symbol before the parameter name.
#include <iostream>
void increment(int* value) {
(*value)++;
}
int main() {
int x = 5;
increment(&x);
std::cout << x << std::endl; // Outputs 6
return 0;
}
In this example, the increment function takes an int value passed by pointer and increments it. When the increment function is called in the main function with the address of the variable x, the value of x is changed and the output is 6.
There are several advantages of using pass-by-reference and pass-by pointer in C++:
Pass by reference allows you to change the value of the original variable, without the need to explicitly dereference the pointer. This can make the code cleaner and easier to read.
Pass by reference is generally faster than pass by pointer since it avoids the overhead of dereferencing the pointer. This can be important in performance-critical code.
Pass by reference allows you to define a function that takes an object of a specific class or struct, and you can use the class's methods and properties directly.
Pass by pointer enables you to pass a null value, whereas pass by reference does not. This can be useful when you need to indicate that a variable is not yet initialized.
Pass by pointer is useful when you are working with dynamically allocated memory. For example, if you want to pass a large data structure to a function, you can pass a pointer to the data structure instead of copying the entire data structure.
Pass by reference can be useful when you want to prevent the function from modifying the original variable by mistake. For example, when passing a const reference, the function can not change the value of the original variable.
In general, it's important to keep in mind that passing by reference can lead to unintended consequences and is not suitable for null or temporary variables.